Getting Started
A step-by-step guide on how to integrate the STRICH SDK into your app and get started with barcode scanning.
Installation
STRICH can be installed in multiple ways, depending on your environment or workflow.
Installing via NPM and a bundler
If you're using a bundler like Vite or esbuild, you can simply install STRICH via NPM.
STRICH uses semantic versioning. By default, npm will add a version requirement of ^x.y.z, which will automatically update the dependency to the latest minor version every time you run npm install.
Loading from a CDN
Alternatively, you can choose to load STRICH from the jsDeliver CDN.
ES6 Modules
Use an import statement to load STRICH as an ES6 module.
The same recommendations apply regarding versioning. To pin a version, change the URL to include the version:
Global object (<script> tag)
If your environment does not support ES6 modules, you can load STRICH with a <script> tag using the non-modular build flavor. The SDK classes will be exposed on a global strich object.
Creating a license key
To initialize the SDK, you need to obtain a license key first. License keys can be created in the Customer Portal after creating an account and starting the free 30-day trial.
License keys are restricted to one or more application URLs (the scope of the license). So if your scanning app will be available at https://app.example.com and you have staging and development environments, you need to add those URLs to the license key when creating it. You can also create separate license keys if you already have a mechanism for injecting per-environment configurations.
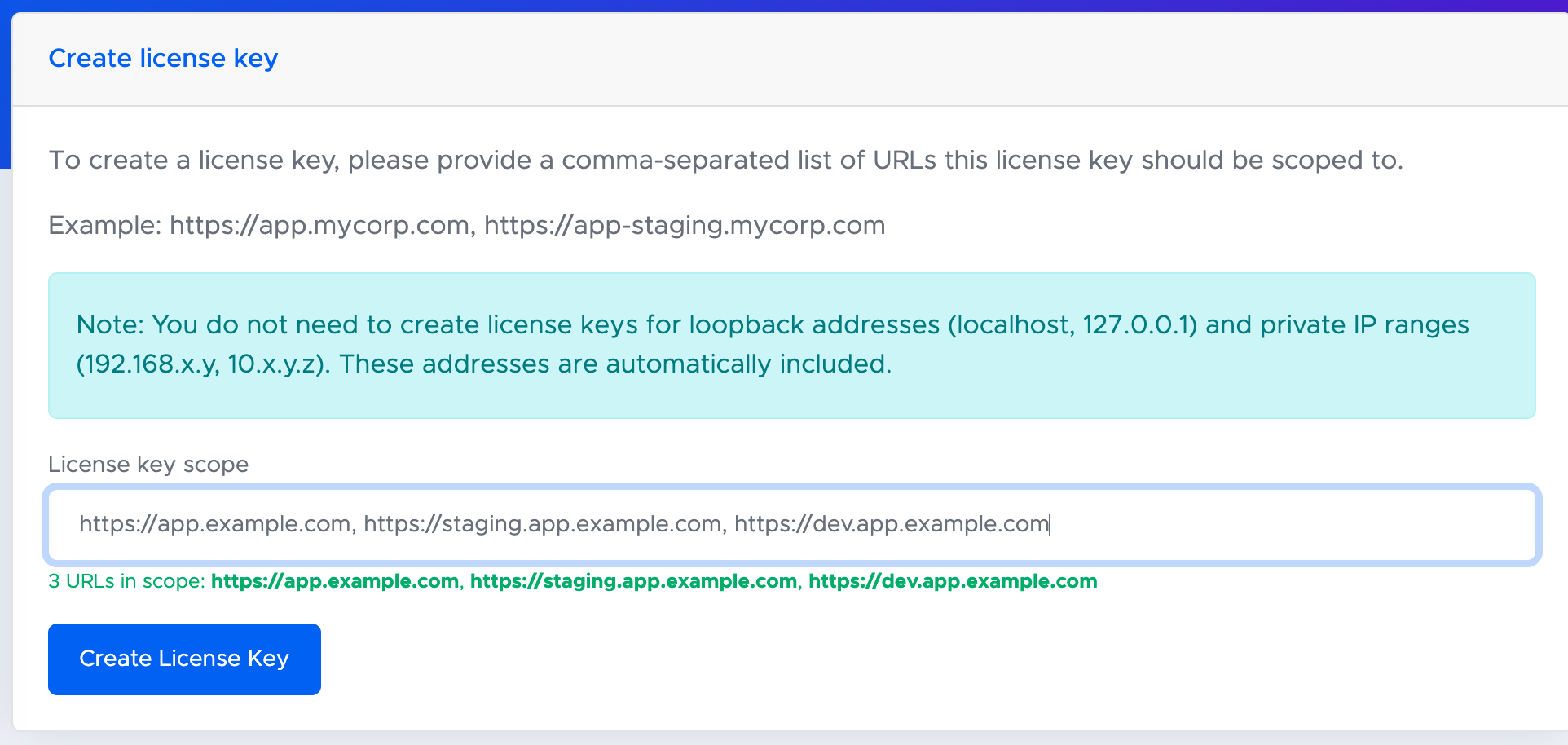
Please note that HTTPS is required. Web browsers only allow access to the camera feed for secure origins. For more information on how to serve from a secure origin during development, please refer to the Deployment Guide.
Initializing the SDK
The SDK needs to be initialized once with the license key created previously by calling StrichSDK.initialize(). When the Promise resolves successfully, the SDK is ready to use.
If initialization fails, the Promise will reject with an SdkError. The message and detailMessage fields should provide an enough information to diagnose the issue. A list of common causes and their remedies is available in our Knowledge Base.
In Single Page Apps (SPAs), we recommend doing the SDK initialization early, before the user expects to see the barcode scanning screen, for instance during the rest of your app initialization. SDK initialization is asynchronous and may require internet connectivity (successful license checks persist up to 48 hours), except for Enterprise licenses which support offline operation as an add-on.
Choosing the Integration
As of version 1.6.0 of the SDK, we now support two kinds of integrations:
BarcodeReader: An embeddable barcode reader that you control. You supply a container in your app UI and are in charge of managing the BarcodeReader. Allows full flexibility in designing your scanning experience.
PopupScanner: An out-of-the-box scanning experience presented in a modal dialog. Perfect for simple scanning use cases that do not require a lot of customization. No changes to your app UI are necessary. Scan barcodes with a single line of code.
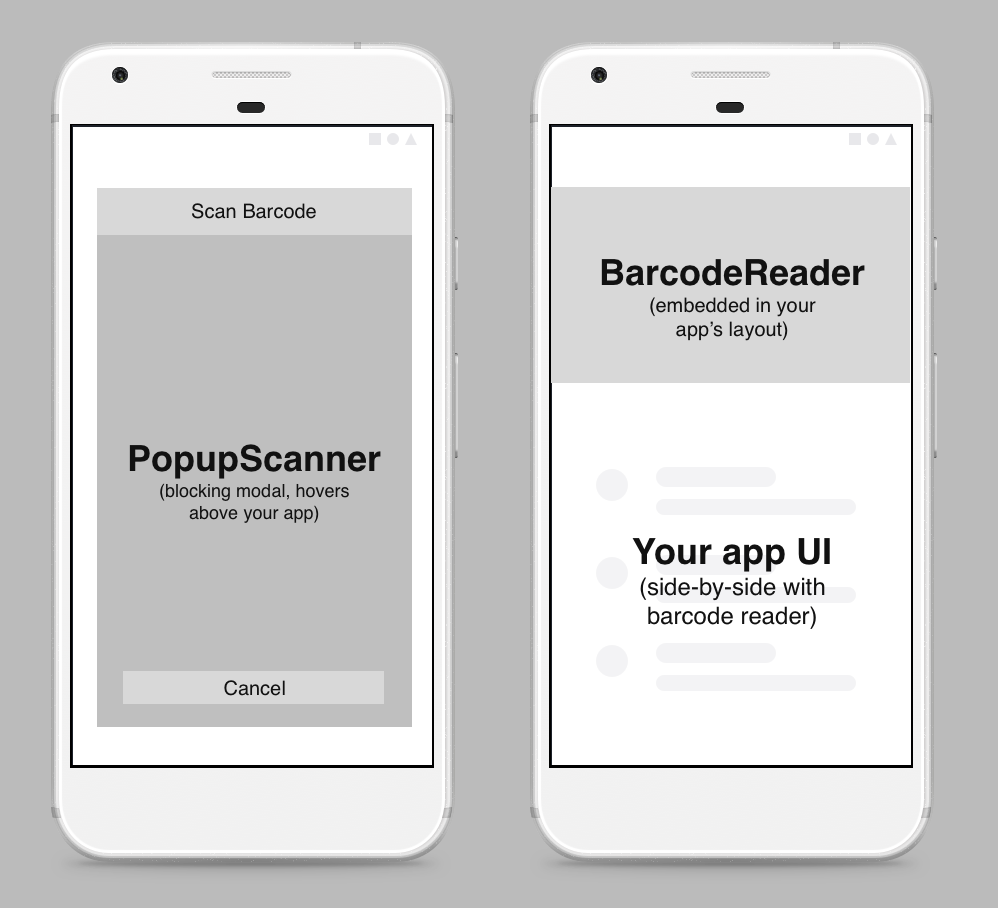
The remainder of this guide will focus on the BarcodeReader integration. Please refer to the PopupScanner documentation if you want to explore that integration, or if you want to quickly verify that the SDK is working.
Integrating the BarcodeReader
Defining the Host Element
We need to provide the BarcodeReader with a place to live. We do so by defining a host element – a DOM element that will contain the UI, i.e. the camera feed, view finder, camera controls, etc.
Example: Vertical Layout with BarcodeReader on Top
A typical scanning app has a vertical layout with the scanner on top, results below and an action bar at the bottom.
Here, the host element is a div with ID scanner, so we can refer to it via the CSS selector #scanner.
Creating a Configuration
Before we can create the BarcodeReader, we need to create a configuration – an object that specifies the functional and visual characteristics of the BarcodeReader.
For a good scanning experience, it is important to restrict the types of barcodes to be detected by the BarcodeReader to only the ones you need. STRICH will automatically set the region of interest (the area where barcodes are detected) to something appropriate for selected barcode types.
Example: Configuration for Code 128 Barcodes
In the example below, we only look for Code 128 barcodes. We also set a duplicateInterval of 2.5 seconds, avoiding repeated scans of the same code over a short time frame.
Initializing the BarcodeReader
Initializing the BarcodeReader is a two-step process: the configuration is passed to the constructor, then the initialize() method is called, which will request access to the camera.
Barcode recognition starts once you call the start() method. To receive barcode detections in your app code, provide a callback using the detected property. The BarcodeReader will invoke this callback whenever barcodes are detected.
Example: Initializing and Starting a BarcodeReader
Camera Access
Initialization requires camera access, which is gated through a browser prompt. It is usually a good idea to make the user aware of this prior to initializing the BarcodeReader, for example by displaying a camera access will be required in the next step notice.
The SDK provides utility functions for determining the current camera permission state and whether the device actually has a camera.
Destroying the BarcodeReader
When you are done with BarcodeReader, it needs to be released by calling the destroy method.
Testing on a Smartphone
STRICH is optimized for barcode scanning in web apps running on smartphones. It is very important to always test your app on actual smartphones.
During development, you are probably running your app locally on your desktop or laptop. When accessing your app from a smartphone on the same network, you might have to do some extra work to set up SSL, as camera access only works if the app is hosted via HTTPS or is accessed via localhost, a secure context.
Please refer to the Deployment Guide for more information about how to expose your app via HTTPS during development.
Next Steps
You are now ready to scan barcodes in your web app. For further advice, check out these additional resources.
API Reference – explore the SDK and its features with our reference documentation.
Deployment Guide – What to know when taking your app live.
Best Practices for Barcode Scanning Apps – Observing these practices ensures a good scanning experience for your users.